Due Wednesday April 3, 2019
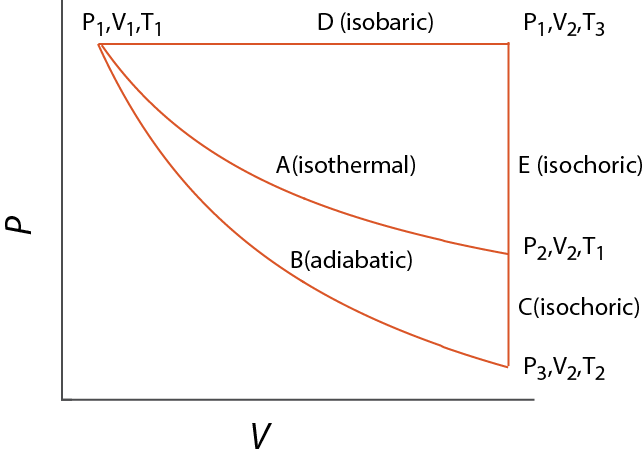
Consider the transformations shown in Fig. 6.3 (reproduced just below) some of these we will discuss in class on 4/3

| step | $P_i$ | $V_i$ | $T_i$ | $P_f$ | $V_f$ | $T_f$ | $\Delta U$ | $w_{rev}$ | $q_{rev}$ | $\Delta S =\int \frac{\delta q_{rev}}{T}$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (isothermal) $V_1\to V_2$ |
$P_1$ | $V_1$ | $T_1$ | $\frac{1}{2}P_1$ | $2 V_1$ | $T_1$ | 0 | $-RT_1 \ln 2$ | $+RT_1 \ln 2$ | $R \ln 2$ |
| B (adiabatic) $V_1\to V_2$ |
$P_1$ | $V_1$ | $T_1$ | $2^{-5/3}P_1$ | $2V_1$ | $\frac{1}{2}^{2/3}T_1$ $=0.630 T_1$ |
$\frac{3}{2}R\left [\left ( \frac{1}{2}\right )^{2/3}-1\right]T_1$ $=-0.555R T_1$ |
$-0.555 RT_1$ | 0 | 0 |
| C (isochoric) $T_1\to T_2$ |
$\frac{1}{2}P_1$ | $2 V_1$ | $T_1$ | $2^{-5/3}P_1$ | $2V_1$ | $T_f=T_2$ $=0.630 T_1$ |
$\frac{3}{2}R (T_2-T_1)$ $=-0.555 R T_1$ |
0 | $-0.555 R T_1$ | $\frac{3}{2} R \int \frac{dT}{T}$ $=\frac{3}{2}R \ln(\frac{1}{2}^{2/3})$ $= - R \ln 2$ |
| D (isobaric) $V_1\to V_2$ |
$P_1$ | $V_1$ | $T_1$ | $P_1$ | $2 V_1$ | $2 T_1$ | $\frac{3}{2} R T_1$ | $-P_1 V_1$ $= -R T_1$ |
$\frac{5}{2}R T_1$ | $R(\frac{3}{2}\int \frac{dt}{T}+ \int \frac{dv}{V})$ $=\frac{5}{2}R \ln 2$ |
| E (isochoric) $T_1\to T_3$ |
$\frac{1}{2}P_1$ | $2 V_1$ | $T_1$ | $P_1$ | $2 V_1$ | $2T_1$ | $\frac{3}{2}R T_1$ | 0 | $\frac{3}{2}R T_1$ | $\frac{3}{2}R \ln 2$ |